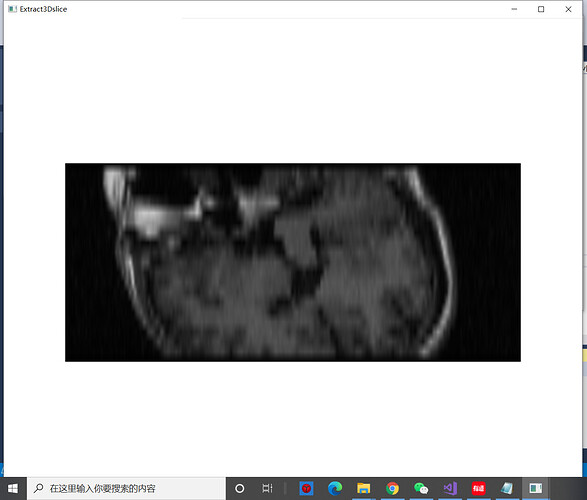
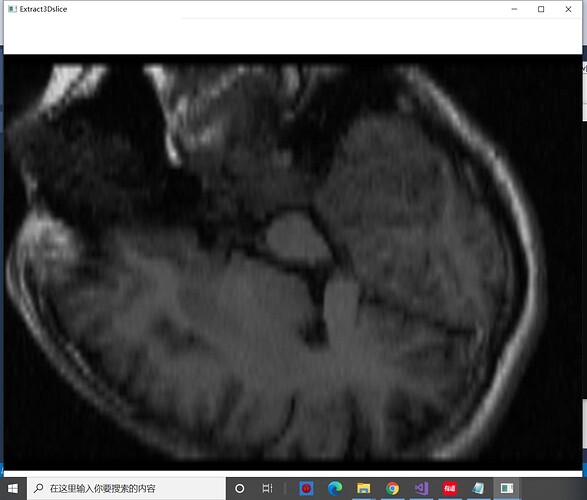
My question is: How do I get a fixed size image?
I use a sensor to control the Angle and make VTK image continuously. But the picture gets bigger and smaller. The problem is the same for both 512×512×24-format 3d data and 194×204×190-format 3D data. These are some of the images I produced when I used 512×512×24-format file.
Here is my code:
#include "vtkAutoInit.h"
VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingOpenGL2);
VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkInteractionStyle);
#include <vtkSmartPointer.h>
#include <vtkImageData.h>
#include <vtkMetaImageReader.h>
#include <vtkMatrix4x4.h> //
#include <vtkImageReslice.h>
#include <vtkLookupTable.h>
#include <vtkImageMapToColors.h>
#include <vtkImageActor.h>
#include <vtkRenderer.h>
#include <vtkRenderWindow.h>
#include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h>
#include <vtkInteractorStyleImage.h>
#include <Python.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
//---------------------------------------------------
//调用python程序
//Py_SetPythonHome(L"C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Microsoft Visual Studio\\Shared\\Python36_64");
/**
这句语句是在添加python.exe所在路径,不添加虽然编译没有问题,但是会在运行时出现
Fatal Python error: initfsencoding: unable to load the file system codec
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'encodings'
这种错误
**/
Py_Initialize();//使用python之前,要调用Py_Initialize();这个函数进行初始化
if (!Py_IsInitialized())
{
printf("初始化失败!");
return 0;
}
else
{
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('./')");//这一步很重要,修改Python路径
PyObject * pModule = NULL;//声明变量
PyObject * pFunc1 = NULL;// 声明变量
PyObject * pFunc2 = NULL;
PyObject * pFunc3 = NULL;
PyObject * pValue = NULL;
pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("WitSensor");//这里是要调用的文件名WitSensor.py
if (pModule == NULL)
{
//如果显示‘没找到该python文件’而没找出问题,有可能是因为此python中的接口设置不对(com3)
cout << "没找到该python文件" << endl;
}
else
{
//pFunc1 = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "get_angle");//这里是要调用的函数名
//pFunc2 = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "DueData");
pFunc3 = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "mainfunc");
pValue = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc3, NULL);//调用函数
float x, y, z;
PyArg_ParseTuple(pValue, "f|f|f", &x, &y, &z);
//**************
vtkSmartPointer<vtkMetaImageReader> reader =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkMetaImageReader>::New();
//vtkImageReader2是vtkMetaImageReader的父类,SetFileName是从vtkImageReader2中继承的
//mhd用来存放信息,raw用来存放数据?
reader->SetFileName("E:\\MyVTKwork\\resource_w\\brain\\brain.mhd");
//vtkAlgorithm←vtkImageAlgorithm←vtkImageReader2←vtkMetaImageReader(继承关系)
reader->Update();
int extent[6];//设置XYZ的范围
double spacing[3];//设置立方体单元格间距
double origin[3];
//在每个轴上,范围extent由第一个点的索引和最后一个点的索引定义。extent按XYZ的顺序存储
//(是不是说extent[0]是x轴范围的起始坐标,extent[1]是x轴范围的结束坐标?后面依次类推?)
//GetOutput():获取此算法上端口的输出数据对象;GetExtent(int [6]):获取数据集的范围
reader->GetOutput()->GetExtent(extent);
//GetSpacing(double [3]):获取组成数据集的立方体单元格的间距(宽度、高度、长度)。
reader->GetOutput()->GetSpacing(spacing);
//GetOrigin(double [3]):获取原点位置(起始点)
reader->GetOutput()->GetOrigin(origin);
//center应该就是中心点,center[0]、center[1]、center[2]应该就是XYZ轴中心点的坐标
double center[3];
//(extent[0]+extent[1])*0.5是x轴范围的中点,再*此轴上的间距spacing[0]就是实际的x轴中点
//yz轴同理
center[0] = origin[0] + spacing[0] * 0.5 * (extent[0] + extent[1]);
center[1] = origin[1] + spacing[1] * 0.5 * (extent[2] + extent[3]);
center[2] = origin[2] + spacing[2] * 0.5 * (extent[4] + extent[5]);
//*****************************************************************//
////斜切面
//static double axialElements[16] = {
// 1, 0, 0, 0,
// 0, 0.866025, -0.5, 0,
// 0, 0.5, 0.866025, 0,
// 0, 0, 0, 1
//};
////平行于XY平面
//static double axialElements[16] = {
// 1, 0, 0, 0,
// 0, 1, 0, 0,
// 0, 0, 1, 0,
// 0, 0, 0, 1
//};
////平行于XZ平面
//static double axialElements[16] = {
// 1, 0, 0, 0,
// 0, 0, 1, 0,
// 0, -1, 0, 0,
// 0, 0, 0, 1
//};
////平行于YZ平面
//static double axialElements[16] = {
// 0, 0,-1, 0,
// 1, 0, 0, 0,
// 0,-1, 0, 0,
// 0, 0, 0, 1
//};
//angle为角度,radian为弧度,C++中cos函数中对应的为弧度值
float x_angle, y_angle, z_angle, x_radian, y_radian, z_radian;
/*cin >> x_angle >> y_angle >> z_angle;*/
x_angle = x;
y_angle = y;
z_angle = z;
float pi = 3.1415926;
x_radian = pi * x_angle / 180;
y_radian = pi * y_angle / 180;
z_radian = pi * z_angle / 180;
//测试平面
//具有一般性的切面
const double axialElements[16] = {
cos(y_radian),cos(x_radian)*cos(z_radian),cos(x_radian),0,
-cos(x_radian),cos(y_radian)*cos(z_radian),cos(y_radian),0,
0,-pow(cos(x_radian),2) - pow(cos(y_radian),2),cos(z_radian),0,
0,0,0,1
};
//平行于XY平面的切面
const double axialElements2[16] = {
1, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1
};
/*static double axialElements[16] = {
cos(y_radian),cos(x_radian)*cos(z_radian),cos(x_radian),0,
-cos(x_radian),cos(y_radian)*cos(z_radian),cos(y_radian),0,
0,-pow(cos(x_radian),2) - pow(cos(y_radian),2),cos(z_radian),0,
0,0,0,1
};*/
/*
关于这个矩阵的一些说明:
首先,最后 1 列是原点坐标;
最后 1 行必须是 0 0 0 1;
第 123 列要相互正交,且遵循右手定则;
第 3 列为切面的法向量;
第 1 列和第 2 列是沿切片平面边缘的单位向量(将切片平面想象为矩形);
*/
vtkSmartPointer<vtkMatrix4x4> resliceAxes =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkMatrix4x4>::New();
//判断是否方向向量的角度是否垂直于XY平面,从而避免正交向量出现0向量
if (x_angle == 90 && y_angle == 90 && z_angle == 0)
{
resliceAxes->DeepCopy(axialElements2);
}
else
{
resliceAxes->DeepCopy(axialElements);
}
/*
vtkMartrix4x4结构:
00 01 02 03 03被赋值为center[0]
10 11 12 13 13被赋值为center[1]
20 21 22 23 23被赋值为center[2]
30 31 32 33
综上所述,最后一列为中心点坐标
(参考资料说矩阵前三列分别表示x、y、z方向向量?)
*/
resliceAxes->SetElement(0, 3, center[0]);
resliceAxes->SetElement(1, 3, center[1]);
resliceAxes->SetElement(2, 3, center[2]);
//vtkImageReslice这个类的作用:沿着一组新的坐标轴重新切割一个物体
vtkSmartPointer<vtkImageReslice> reslice =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkImageReslice>::New();
//SetInputConnection:为给定的输入端口索引设置连接
reslice->SetInputConnection(reader->GetOutputPort());
//SetOutputDimensionality:强制输出的维度为1、2、3或0(默认为3),此例中是2
reslice->SetOutputDimensionality(2);
//SetResliceAxes:设置输出体素的坐标轴
/*
矩阵的第一列指定x轴向量(第四个元素必须设置为0),第二列指定y轴,第三列指定z轴;
第四列是坐标轴的原点(第四个元素必须设置为1)
(以上是官方说明,可以说第四行元素要设置为0 0 0 1)
*/
reslice->SetResliceAxes(resliceAxes);
//SetInterpolationModeToLinear()指定了切面提取中的差值方式为线性差值;此外还有其他插值
reslice->SetInterpolationModeToLinear();
//*****************************************************************//
//vtkLookupTable:通过查找表把标量值映射为颜色
vtkSmartPointer<vtkLookupTable> colorTable =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkLookupTable>::New();
colorTable->SetRange(0, 1000); //设置要映射的标量范围
colorTable->SetValueRange(0.0, 1.0); //设置值中的范围,取值范围[0,1]
colorTable->SetSaturationRange(0.0, 0.0); //设置饱和度范围
colorTable->SetRampToLinear(); //将表格坡道的形状设置为线性
colorTable->Build(); //从色调,饱和度,值,alpha最小/最大值生成查找表
//vtkImageMapToColors:通过查找表映射输入图像
vtkSmartPointer<vtkImageMapToColors> colorMap =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkImageMapToColors>::New();
colorMap->SetLookupTable(colorTable); //设置查找表
colorMap->SetInputConnection(reslice->GetOutputPort()); //为给定的输入端口索引设置连接
colorMap->Update();
//*****************************************************************//
//vtkImageActor:在渲染的3D场景中绘制图像
vtkSmartPointer<vtkImageActor> imgActor =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkImageActor>::New();
imgActor->SetInputData(colorMap->GetOutput()); //设置图像数据输入
vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer> renderer =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New(); //渲染器
renderer->AddActor(imgActor); //向渲染器中添加不同类型的道具(这里是vtkImageActor类型的)
renderer->SetBackground(1.0, 1.0, 1.0); //使用rgb颜色规范,设置渲染屏幕的背景颜色
//vtkRenderWindow:为渲染器创建一个绘图窗口
vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow> renderWindow =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow>::New();
renderWindow->AddRenderer(renderer); //将渲染器添加到渲染器列表中
renderWindow->Render(); //要求这个RenderWindow拥有的每个渲染器渲染它的图像并同步这个过程
renderWindow->SetSize(1000, 1000); //以屏幕坐标(像素为单位)设置渲染窗口的大小(宽度和高度)
renderWindow->SetWindowName("Extract3Dslice"); //渲染窗口的名称
while (1)
{
pValue = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc3, NULL);//调用函数
PyArg_ParseTuple(pValue, "f|f|f", &x, &y, &z);
x_radian = pi * x / 180;
y_radian = pi * y / 180;
z_radian = pi * z / 180;
const double axialElements[16] = {
cos(y_radian),cos(x_radian)*cos(z_radian),cos(x_radian),0,
-cos(x_radian),cos(y_radian)*cos(z_radian),cos(y_radian),0,
0,-pow(cos(x_radian),2) - pow(cos(y_radian),2),cos(z_radian),0,
0,0,0,1
};
if (x_angle == 90 && y_angle == 90 && z_angle == 0)
{
resliceAxes->DeepCopy(axialElements2);
}
else
{
resliceAxes->DeepCopy(axialElements);
}
resliceAxes->SetElement(0, 3, center[0]);
resliceAxes->SetElement(1, 3, center[1]);
resliceAxes->SetElement(2, 3, center[2]);
reslice->SetResliceAxes(resliceAxes);
reslice->Update();
colorMap->SetInputConnection(reslice->GetOutputPort()); //为给定的输入端口索引设置连接
colorMap->Update();
imgActor->SetInputData(colorMap->GetOutput()); //设置图像数据输入
//vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer> renderer =
// vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New(); //渲染器
renderer->AddActor(imgActor); //向渲染器中添加不同类型的道具(这里是vtkImageActor类型的)
//renderer->SetBackground(1.0, 1.0, 1.0); //使用rgb颜色规范,设置渲染屏幕的背景颜色
renderWindow->AddRenderer(renderer); //将渲染器添加到渲染器列表中
renderWindow->Render(); //要求这个RenderWindow拥有的每个渲染器渲染它的图像并同步这个过程
//renderer->Delete();
}
reader->Delete();
resliceAxes->Delete();
reslice->Delete();
colorTable->Delete();
colorMap->Delete();
imgActor->Delete();
renderer->Delete();
renderWindow->Delete();
}
Py_Finalize();//调用Py_Finalize,这个和Py_Initialize相对应的。
}
system("pause");
//---------------------------------------------------
return 0;
}
The Python file is what I use to read the sensor Angle.
This is my first time using VTK community and my English needs improving.
Finally, thank you for your help.
supplement:
If I create vtkSmartPointer renderer repeatedly in while(1), the image will display more normally. But it only lasted a few seconds, because I didn’t destroy it. But renderWindow always needs a renderer to use.