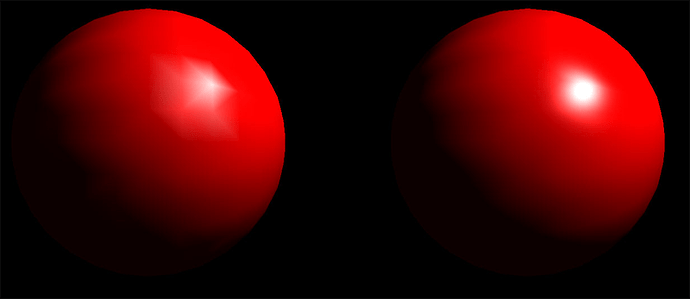
I see a clear difference between flat interpolation and Gouraud/Phong, but the two latter look pixel-identical to me. I’ve tried with specular=1, high and low specular powers, and still can’t spot any difference, except that the vtkOpenGLProperty object reports it’s using one or the other. Is there any requirement from the graphics driver? Any particular setting where I could see their difference? Sample images?
Gourand computes post lit color at the points, then interpolates the color across the cell. Phong interpolates the normal across the cell computing post lit colors at many places across the cell.
There is a difference between the" phong lighting model" and “phong shading”.
I’m aware of the theoretical differences, and the picture does indeed show a clear difference. However, I still don’t see any difference in my local renderings, they both look more like right ball (which I believe is Phong). Can you see any difference with this?
import vtk
# create a rendering window and renderer
ren = vtk.vtkRenderer()
renWin = vtk.vtkRenderWindow()
renWin.AddRenderer(ren)
# create a renderwindowinteractor
iren = vtk.vtkRenderWindowInteractor()
iren.SetRenderWindow(renWin)
# create source
source = vtk.vtkSphereSource()
source.SetCenter(0,0,0)
source.SetRadius(5.0)
# mapper
mapper = vtk.vtkPolyDataMapper()
if vtk.VTK_MAJOR_VERSION <= 5:
mapper.SetInput(source.GetOutput())
else:
mapper.SetInputConnection(source.GetOutputPort())
# actor
actor = vtk.vtkActor()
actor.SetMapper(mapper)
actor.GetProperty().SetDiffuseColor(1,0,0)
actor.GetProperty().SetDiffuse(1)
actor.GetProperty().SetSpecular(1)
actor.GetProperty().SetSpecularPower(30.0)
#actor.GetProperty().SetInterpolationToGouraud()
actor.GetProperty().SetInterpolationToPhong()
# assign actor to the renderer
ren.AddActor(actor)
light = vtk.vtkLight()
light.SetPosition(10, 10, 10)
light.SetColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
light.SetLightTypeToCameraLight()
#ren.AutomaticLightCreationOff()
ren.AddLight(light)
# enable user interface interactor
iren.Initialize()
iren.SetInteractorStyle(vtk.vtkInteractorStyleTrackballCamera())
renWin.Render()
iren.Start()
I’m running VTK 8.1.0, with python 2.7 or 3.4, on an Intel integrated graphics card (Ubuntu 14.04).
Set the tesselatiaon of your sphere source to a very small number, like 6, and you should see a difference.
It’s already quite small (the default, 8), setting it to 6 or 3 doesn’t bring up any difference. If I understand it correctly, with Gouraud I shouldn’t be able to see a small highlight in the center of a large triangular face, with its 3 corners highlight-less… well, I see it, just the same as with Phong. For more information, I’m using the VTK installed through pip.
I have the same confusion. Looks exactly the same, even though I’ve set the low resolution.
import vtk
def create_sphere_actor(shading_type="gouraud"):
sphere = vtk.vtkSphereSource()
sphere.SetRadius(1.0)
sphere.SetThetaResolution(10) # 经度分辨率
sphere.SetPhiResolution(10) # 纬度分辨率
# 创建mapper
mapper = vtk.vtkPolyDataMapper()
mapper.SetInputConnection(sphere.GetOutputPort())
# 创建actor
actor = vtk.vtkActor()
actor.SetMapper(mapper)
# 设置材质属性
property = actor.GetProperty()
property.SetColor(0.8, 0.2, 0.2) # 红色
property.SetSpecular(0.8) # 镜面反射强度
property.SetSpecularPower(30) # 镜面反射锐度
property.SetDiffuse(0.8) # 漫反射强度
property.SetAmbient(0.1) # 环境光强度
# 设置着色方式
if shading_type.lower() == "gouraud":
property.SetInterpolationToGouraud()
elif shading_type.lower() == "phong":
property.SetInterpolationToPhong()
else:
property.SetInterpolationToFlat()
return actor
def create_text_actor(text, position):
text_source = vtk.vtkVectorText()
text_source.SetText(text)
mapper = vtk.vtkPolyDataMapper()
mapper.SetInputConnection(text_source.GetOutputPort())
actor = vtk.vtkActor()
actor.SetMapper(mapper)
actor.SetPosition(position)
actor.SetScale(0.2, 0.2, 0.2)
actor.GetProperty().SetColor(1, 1, 1) # 白色文本
return actor
def main():
"""主函数:创建并显示Gouraud vs Phong着色对比"""
# 创建渲染器
renderer = vtk.vtkRenderer()
renderer.SetBackground(0.1, 0.1, 0.2) # 深蓝色背景
# 创建Gouraud着色的球体
gouraud_sphere = create_sphere_actor("gouraud")
gouraud_sphere.SetPosition(-2, 0, 0) # 左侧位置
renderer.AddActor(gouraud_sphere)
# 创建Phong着色的球体
phong_sphere = create_sphere_actor("phong")
phong_sphere.SetPosition(2, 0, 0) # 右侧位置
renderer.AddActor(phong_sphere)
# 添加文本标签
gouraud_label = create_text_actor("Gouraud Shading", (-2.5, -1.5, 0))
phong_label = create_text_actor("Phong Shading", (1.5, -1.5, 0))
renderer.AddActor(gouraud_label)
renderer.AddActor(phong_label)
# 设置光源
light = vtk.vtkLight()
light.SetPosition(5, 5, 5)
light.SetFocalPoint(0, 0, 0)
light.SetColor(1, 1, 1)
light.SetIntensity(1.0)
renderer.AddLight(light)
# 创建渲染窗口
render_window = vtk.vtkRenderWindow()
render_window.AddRenderer(renderer)
render_window.SetSize(800, 400)
render_window.SetWindowName("Gouraud vs Phong 着色对比")
# 创建交互器
interactor = vtk.vtkRenderWindowInteractor()
interactor.SetRenderWindow(render_window)
# 设置相机位置
camera = renderer.GetActiveCamera()
camera.SetPosition(0, 0, 8)
camera.SetFocalPoint(0, 0, 0)
camera.SetViewUp(0, 1, 0)
# 开始渲染和交互
render_window.Render()
interactor.Start()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
To answer the original question, VTK uses exactly the same shader code for SetInterpolationToGouraud() and SetInterpolationToPhong().
Both choices provide shading that seems to be Phong-ish, that is, something close to Phong shading but probably not exactly Phong shading.